Facing the demand of the development of electronic components such as the third-generation semiconductor switching power supply and integrated inductor for high-performance soft magnetic materials such as high frequency, high permeability, high temperature resistance and high voltage resistance materials. Aiming at the problems that traditional metal soft magnetic materials such as micro/nano powder are difficult to obtain, large high frequency loss, and cannot achieve high cut-off frequency and high permeability at the same time. Through the development of micro-nano composite soft magnetic materials, powder preparation technology and equipment, the technical bottleneck of development and application of high-frequency, high temperature resistance and voltage resistance soft magnetic materials is broken through, and the mass production and application of high-performance micro-nano composite soft magnetic materials and devices are realized.
This direction focuses on micro-nano composite soft magnetic materials and devices, including:
1. The evolution and regulation of physical properties of magnetoelectric functional materials and devices under the action of nanoparticles are studying. The research goal is to obtain the relationship between magnetoelectric properties and microstructure of materials, and to obtain the influence law and regulation mechanism of nanoparticles on magnetoelectric properties (magnetic anisotropy, coercivity, high frequency permeability and loss) of micro-nano composite soft magnetic materials. Break through the technical bottleneck of development and application of high-frequency soft magnetic materials.
2. Study on insulation coating technology of metal soft magnetic powder.
3. Development of soft magnetic materials with corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance and high thermal stability and their application in miniature modeling inductors.
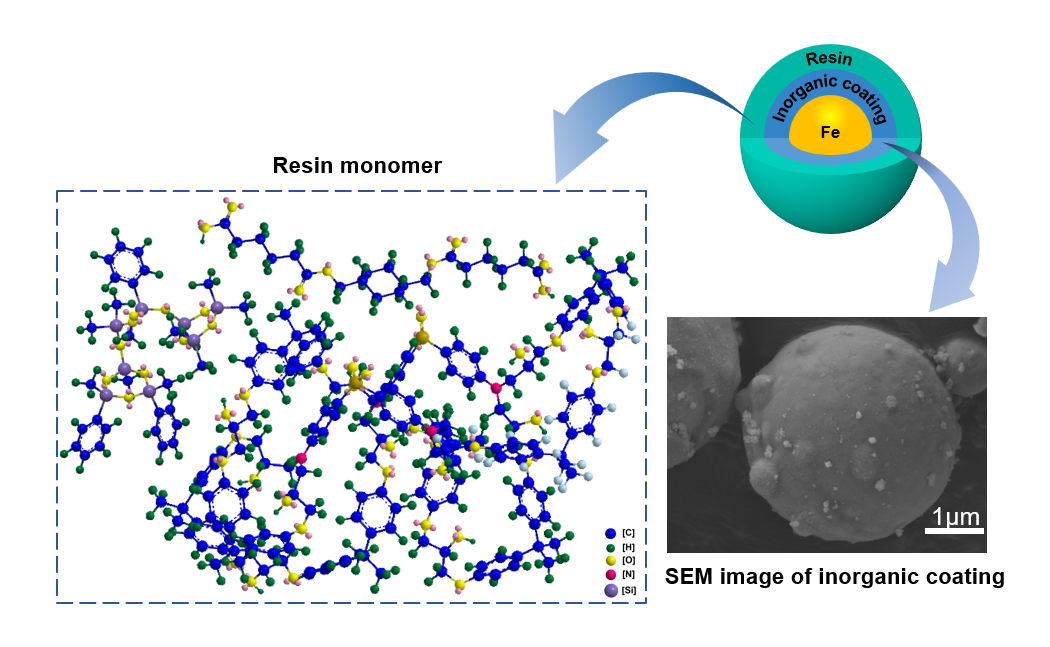
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of insulation cladding

Fig. 2. Miniature integrated moulded inductor

